The extraction of wisdom teeth is a common dental procedure, often necessitated by issues such as impaction or overcrowding. Yet, a pertinent query that surfaces among those undergoing this procedure is: How long does it take for wisdom teeth to heal? While the typical healing period ranges from a few days to several weeks, several factors can influence this timeline. Factors such as the complexity of the extraction, the number of teeth removed, and individual healing capabilities all contribute to the duration of recovery. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring proper post-operative care and optimizing the healing process. We will explore these details further at the end of this article to provide comprehensive insights into the healing journey of wisdom teeth extraction.
What is Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of molars that typically appear in the late teenage years or early twenties. These teeth are located at the back of the mouth, with two on the top and two on the bottom. They are called “wisdom teeth” because they usually come in at a more mature age, when a person is considered to be gaining wisdom. Unlike the other teeth, wisdom teeth often do not have enough space to emerge properly, which can lead to impaction, crowding, and other dental issues.
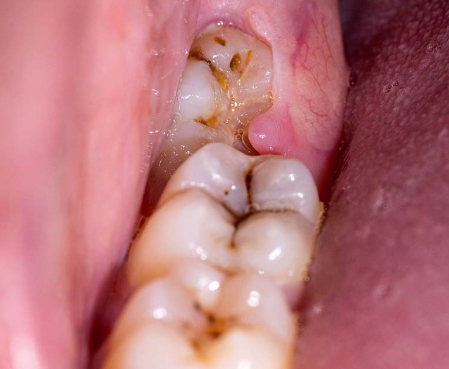
Different Types of Wisdom Teeth
Understanding the different types of wisdom teeth is essential, especially if you are experiencing dental issues related to them. The main types of wisdom teeth are based on their position and the way they emerge or remain within the jawbone. Here are the primary categories:
1. Erupted Wisdom Teeth
Erupted wisdom teeth have fully emerged through the gum line and are visible in the mouth. They are aligned properly with the other teeth and do not cause problems if they are healthy and maintain a good position. Proper dental hygiene can help keep erupted wisdom teeth in good condition.
2. Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Impacted wisdom teeth are those that do not fully emerge through the gum line. They may remain completely buried in the gum and jawbone or partially emerge. Impacted wisdom teeth can cause various issues, including pain, swelling, and infection. There are several subcategories of impacted wisdom teeth based on their position and degree of impaction:
- Soft Tissue Impaction: The tooth has partially emerged through the gum, but the gum still partially covers it. This can lead to gum infection and swelling.
- Partial Bony Impaction: The tooth has partially emerged through the gum and is partially covered by the jawbone. This can cause pain, crowding, and other dental issues.
- Complete Bony Impaction: The tooth is entirely encased within the jawbone and has not emerged through the gum. This can be more complex and often requires surgical extraction.
3. Mesioangular Impaction
Mesioangular impaction is when the wisdom tooth is angled forward, towards the front of the mouth. This is the most common type of impaction. The angle can vary, and the tooth can press against the second molar, causing discomfort and potential damage to adjacent teeth.
4. Distoangular Impaction
Distoangular impaction is when the wisdom tooth is angled backward, towards the back of the mouth. This type of impaction is less common and can be more challenging to remove due to the position of the tooth.
5. Vertical Impaction
Vertical impaction occurs when the wisdom tooth is in an upright position but does not fully emerge through the gum line. It may not always cause issues but can still lead to problems like crowding or improper alignment of other teeth.
6. Horizontal Impaction
Horizontal impaction is when the wisdom tooth is lying on its side within the jawbone. This position can cause significant discomfort and damage to adjacent teeth. Horizontal impactions almost always require surgical intervention for removal.
Understanding these different types of wisdom teeth is crucial for identifying potential dental problems and determining the appropriate treatment. Regular dental check-ups and X-rays can help monitor the development and position of wisdom teeth, allowing for timely intervention if necessary.
Symptoms of Wisdom Teeth Issues
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, can cause various symptoms when they encounter problems during eruption or if they become impacted. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and management of potential issues. Here are common symptoms associated with wisdom teeth problems:
1. Pain or Discomfort
One of the most noticeable symptoms of wisdom teeth issues is pain or discomfort in the back of the mouth or jaw. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent. It can be localized around the wisdom teeth or radiate to nearby areas, such as the ear or jaw.
2. Swelling
Swelling of the gums around the wisdom teeth is another common symptom. Inflammation can occur due to impaction, infection, or irritation caused by partially erupted teeth. Swelling may be accompanied by tenderness, redness, and warmth in the affected area.
3. Difficulty Opening the Mouth
Impacted wisdom teeth can cause limited jaw movement, making it challenging to open the mouth fully. This symptom, known as trismus, can result from inflammation, muscle stiffness, or pain associated with wisdom teeth issues.
4. Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste
Decay, infection, or trapped food particles around wisdom teeth can lead to bad breath (halitosis) or an unpleasant taste in the mouth. These symptoms may persist despite regular oral hygiene practices and can indicate underlying dental issues.

5. Difficulty Chewing or Biting
Pain or discomfort while chewing or biting down can indicate problems with wisdom teeth. Impacted or partially erupted teeth may interfere with normal chewing function, leading to discomfort or difficulty eating certain foods.
6. Jaw Stiffness or Soreness
Wisdom teeth problems can cause jaw stiffness or soreness, especially upon waking up in the morning or after periods of prolonged rest. This symptom may be due to muscle tension, inflammation, or pressure exerted by impacted teeth on surrounding tissues.
7. Headaches or Earaches
Pain from wisdom teeth issues can radiate to other areas of the head and face, leading to headaches or earaches. The pain may be dull or throbbing and can worsen with jaw movement or pressure on the affected side.
8. Swollen Lymph Nodes
In cases of infection or inflammation around wisdom teeth, nearby lymph nodes may become swollen and tender to the touch. Swollen lymph nodes, particularly those under the jaw or in the neck, can indicate an immune response to underlying dental issues.
9. Visible Signs of Infection
In severe cases of infection or abscess formation, visible signs such as pus drainage, fever, or facial swelling may occur. These symptoms require immediate dental attention to prevent complications and systemic spread of infection.
Recognizing these symptoms of wisdom teeth issues can help individuals seek appropriate dental care and treatment promptly. Early intervention can prevent further complications and alleviate discomfort associated with problematic wisdom teeth. Regular dental check-ups and X-rays are essential for monitoring the development and position of wisdom teeth and detecting potential issues before they escalate.
Precautions for Wisdom Teeth
Taking precautions can help minimize the risk of developing issues related to wisdom teeth and promote overall oral health. Here are some essential precautions to consider:
1. Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule regular dental check-ups with your dentist, who can monitor the development and position of your wisdom teeth through clinical examination and X-rays. Early detection of potential problems allows for timely intervention and prevents complications.
2. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Practice good oral hygiene habits, including brushing your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. Proper oral hygiene helps prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria around the wisdom teeth, reducing the risk of decay, gum disease, and infection.
3. Monitor Symptoms
Be vigilant for any symptoms associated with wisdom teeth issues, such as pain, swelling, difficulty chewing, or jaw stiffness. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, consult your dentist promptly for evaluation and appropriate management.
4. Avoid Delayed Treatment
Do not ignore symptoms or delay seeking dental care if you suspect problems with your wisdom teeth. Early intervention can prevent complications and alleviate discomfort associated with impacted or problematic wisdom teeth.
5. Orthodontic Assessment
Undergo an orthodontic assessment to evaluate the alignment of your teeth and the potential impact of wisdom teeth on your bite. Orthodontic treatment may be recommended to address crowding or misalignment issues, which can be exacerbated by the eruption of wisdom teeth.
6. Consider Extraction
Discuss with your dentist or oral surgeon whether extraction of your wisdom teeth is advisable, especially if they are impacted, causing pain, or at risk of developing complications. Extraction may be recommended as a preventive measure to avoid future problems.
7. Follow Post-Extraction Care Instructions
If you undergo wisdom teeth extraction, follow your dentist’s post-operative instructions carefully to promote proper healing and prevent complications. This may include avoiding strenuous activities, sticking to a soft diet, practicing good oral hygiene, and taking prescribed medications as directed.
8. Attend Follow-up Appointments
Attend follow-up appointments with your dentist or oral surgeon as scheduled to ensure that your wisdom teeth extraction site is healing properly and to address any concerns or complications that may arise.
9. Maintain Overall Health
Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding habits such as smoking, which can impair healing and increase the risk of complications after wisdom teeth extraction.
10. Stay Informed
Stay informed about oral health topics and advancements in dental care by consulting reputable sources, asking questions during dental appointments, and staying proactive about your oral health needs.
By following these precautions, you can help minimize the likelihood of experiencing issues related to wisdom teeth and maintain optimal oral health throughout your life.
Treatment of Wisdom Teeth
The treatment of wisdom teeth varies depending on factors such as the position, orientation, and condition of the teeth, as well as the presence of symptoms or complications. Here are the common treatment options for addressing issues related to wisdom teeth:
1. Monitoring
In cases where wisdom teeth are healthy, properly aligned, and not causing any symptoms or problems, the dentist may recommend regular monitoring through periodic dental check-ups and X-rays. Monitoring allows the dentist to track the development and position of the wisdom teeth and intervene if issues arise in the future.
2. Conservative Management
For minor symptoms or early-stage problems associated with wisdom teeth, conservative management techniques may be employed to alleviate discomfort and promote oral health. This may include measures such as:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with wisdom teeth issues.
- Oral Irrigation: Rinsing the mouth with warm saltwater can help reduce inflammation and promote healing around the wisdom teeth.
- Topical Treatments: Applying numbing gels or oral antiseptics to the affected area can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
3. Extraction
Extraction is the most common treatment for problematic wisdom teeth, especially if they are impacted, causing pain, infection, or other complications. Extraction may be performed by a dentist or oral surgeon and can involve one of the following approaches:
- Simple Extraction: This involves removing fully erupted wisdom teeth that are visible in the mouth. The dentist or oral surgeon loosens the tooth with instruments and extracts it using forceps.
- Surgical Extraction: Surgical extraction is necessary for impacted wisdom teeth that are partially or fully covered by gum tissue or jawbone. The oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum, removes any bone blocking access to the tooth, and then extracts the tooth in sections if necessary.
4. Orthodontic Treatment
In cases where wisdom teeth contribute to dental crowding or misalignment, orthodontic treatment may be recommended to address these issues. Orthodontic interventions such as braces or clear aligners can help realign the teeth and create space in the dental arch, potentially alleviating symptoms associated with impacted or crowded wisdom teeth.
5. Treatment of Complications
Complications associated with wisdom teeth, such as infections, cysts, or damage to adjacent teeth, may require specific treatments tailored to the individual’s needs. This may involve procedures such as root canal therapy, periodontal treatment, or surgical intervention to address the underlying issue and restore oral health.
6. Preventive Measures
For individuals at risk of developing wisdom teeth-related problems, preventive measures such as early intervention, regular dental check-ups, and proper oral hygiene practices are essential. Early detection and management of issues can help prevent complications and minimize the need for extensive treatment in the future.
The choice of treatment for wisdom teeth depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the presence of complications, and the individual’s overall oral health. Dentists work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans that address their specific needs and promote optimal oral health and well-being.
How Long Does It Take for Wisdom Teeth to Heal?
The healing process after wisdom teeth removal typically takes about one to two weeks, although individual experiences may vary. Here’s a general timeline of the healing stages:
1. Immediate Post-Operative Period (First 24-48 Hours):
- Right after the extraction procedure, patients may experience some bleeding, swelling, and discomfort.
- Patients are advised to bite down on gauze pads placed over the extraction sites to control bleeding and promote blood clot formation.
- Swelling around the extraction sites and in the cheeks may peak within the first 24 to 48 hours.
- Discomfort and soreness are common during this period and can be managed with prescribed or over-the-counter pain medication as directed by the dentist or oral surgeon.
2. Days 2-3:
- Swelling and discomfort gradually begin to subside.
- Patients may continue to experience some minor bleeding, particularly when rinsing the mouth or performing oral care routines.
- It’s important to follow post-operative instructions provided by the dental professional, including avoiding certain foods, activities, and oral hygiene practices to promote proper healing.
3. Days 4-7:
- Swelling further decreases, and any bruising may begin to fade.
- Discomfort and soreness diminish, although some sensitivity may persist, especially when chewing or touching the extraction sites.
- Patients can gradually resume a soft diet, starting with easily chewable foods and gradually reintroducing firmer textures as tolerated.
- Oral hygiene routines can be resumed, but patients should be gentle around the extraction sites to avoid disrupting the healing process.
4. Week 2:
- By the end of the second week, most patients experience significant improvement in swelling, discomfort, and oral function.
- Any remaining stitches (if used) may be removed during a follow-up appointment with the dentist or oral surgeon.
- Patients should continue to monitor their healing progress and report any unusual symptoms or concerns to their dental provider.
It’s essential for patients to follow all post-operative instructions provided by their dentist or oral surgeon to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications. While the majority of healing occurs within the first two weeks after wisdom teeth removal, complete healing of the extraction sites may take several weeks to months.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about wisdom teeth, along with their answers:
They are called wisdom teeth because they usually erupt during a time in life when a person is considered to be more mature or “wiser” than they were as a child.
Wisdom teeth inflammation typically resolves within a few days to a week with proper oral hygiene and symptom management.
Chronic trismus after wisdom teeth removal refers to persistent difficulty opening the mouth fully, often due to prolonged muscle stiffness or spasms in the jaw muscles. It can occur as a complication of wisdom teeth extraction and may require physical therapy or other interventions for management.
Not everyone develops wisdom teeth. Some individuals may have one, two, three, or even none at all. The presence and development of wisdom teeth vary from person to person.
Wisdom teeth may need to be removed if they are causing pain, swelling, infection, or other complications. Additionally, if they are impacted, crowding other teeth, or at risk of developing problems in the future, extraction may be recommended.
While discomfort during the recovery period is common, wisdom teeth removal itself is not typically painful due to the use of anesthesia or sedation during the procedure. Dentists and oral surgeons take steps to ensure that patients are as comfortable as possible during extraction.
Conclusion
The healing time for wisdom teeth extraction varies based on several factors, but most people can expect significant healing within two weeks and complete recovery within three to six months. By following proper aftercare instructions and being mindful of potential complications, you can ensure a smooth and successful recovery.










Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.